Overview of Core Production Processes and Key Equipment for Railway Signal Cables – Chinese Technology Solutions Support Indian Railway Upgrades
As India's railway network transitions towards digitalization and high-speed operation, stringent requirements are placed on the anti-interference capability, stability, and safety of railway signal cables. China, with over a decade of technological accumulation in the field of railway signal cables, has developed mature, full-process solutions ranging from insulated single-wire manufacturing to finished product testing. The precision of its process control, level of equipment automation, and product reliability have been validated through numerous high-speed rail projects worldwide. Based on years of practical experience, this article outlines key points sequentially according to the production process, providing actionable technical references for Indian manufacturers to help them overcome production bottlenecks and enhance product competitiveness.
I. Basic Process: Insulated Single Wire Manufacturing—The "First Line of Defense" for Cable Quality
The insulated single wire is the core for signal transmission in railway signal cables. Its uniformity directly determines the quality of subsequent
processes. The Chinese technical solution ensures stable and controllable single-wire performance through a triple approach of "Material Control + Process Optimization + Equipment Assurance."
(A) Core Process Control Points

-
Conductor Quality Control:
-
High-purity electrolytic copper (purity ≥99.95%) is selected. Copper wire diameter deviation is precisely controlled (±0.01 mm) through drawing dies, while annealing current stability is monitored (fluctuation ≤ ±5 A) to ensure uniform elongation (range 15%-20%). This prevents core misalignment during subsequent stranding due to uneven copper wire softness/hardness, which affects capacitance balance.
-
The commonly used "Integrated Drawing-Annealing Production Line" by Chinese manufacturers enables coordinated control of drawing speed (up to 1200 m/min) and annealing temperature (380-420°C). The resulting copper wire surface smoothness reaches Ra ≤0.8 μm, far exceeding the Ra ≤1.6 μm standard of traditional Indian equipment.
-
-
Insulation Layer Extrusion Control:
-
A "Skin-Foam-Skin" three-layer physical foam structure (inner PE layer, middle foam layer, outer PE layer) is adopted. A precision extruder (screw speed fluctuation ≤ ±1 rpm) controls insulation outer diameter deviation (±0.05 mm) and concentricity (≥90%), with foam stability maintained at 60%-70%. This structure reduces cable dielectric loss by 30% and improves impact resistance by 25%.
-
Key control points: Preheating temperature requires segmented control (feed zone 160°C, melting zone 200°C, homogenizing zone 190°C) to avoid bubbles or collapse in the foam layer. Simultaneously, an online capacitance monitor (accuracy ±0.1 pF/m) provides real-time feedback on insulation layer uniformity, allowing for timely adjustment of extrusion parameters.
-
-
Cleanliness and Die Maintenance:
-
The Chinese solution emphasizes "Process Cleanliness Control": Replace the drawing emulsion filter cloth every 8 hours; clean the annealing cooling water pipes daily to prevent copper powder or impurities from adhering to the copper wire surface.
-
Drawing dies use polycrystalline diamond material (hardness HV≥8000), with a service life 5 times that of traditional dies. Furthermore, die wear inspection is performed after every 500 km of single-wire production (using a laser diameter gauge; replace immediately if deviation exceeds 0.02 mm), eliminating the problem of "uneven thickness" at the source.
-
(B) Key Equipment Recommendations
The Chinese independently developed "JYL-1250 Insulated Single Wire Extrusion Production Line," which integrates the following core modules:
-
Online Laser Diameter Gauge: Monitors single-wire outer diameter in real time, synchronizing data to the PLC control system for automatic extruder speed adjustment.
-
Closed-loop Foam Degree Control System: Controls nitrogen injection volume via pressure sensors (accuracy ±0.01 MPa) to ensure uniform foam layer density.
-
Precise Color Masterbatch Dosing Device: Color masterbatch addition error ≤ ±0.1%, preventing identification errors in subsequent processes due to uneven coloring.
II. Core Process: Star Quad Formation and Copper Shielding—The "Core Guarantee" of Anti-Interference Performance
The star quad (star-stranding of 4 insulated single wires) and copper shielding are critical links for enhancing cable anti-interference capability. Addressing common pain points in Indian manufacturing, such as "unstable stranding pitch," "copper tape edge lift," and "drain wire breakage," the Chinese technical solution provides systematic countermeasures.
(A) Star Quad Manufacturing Process Points
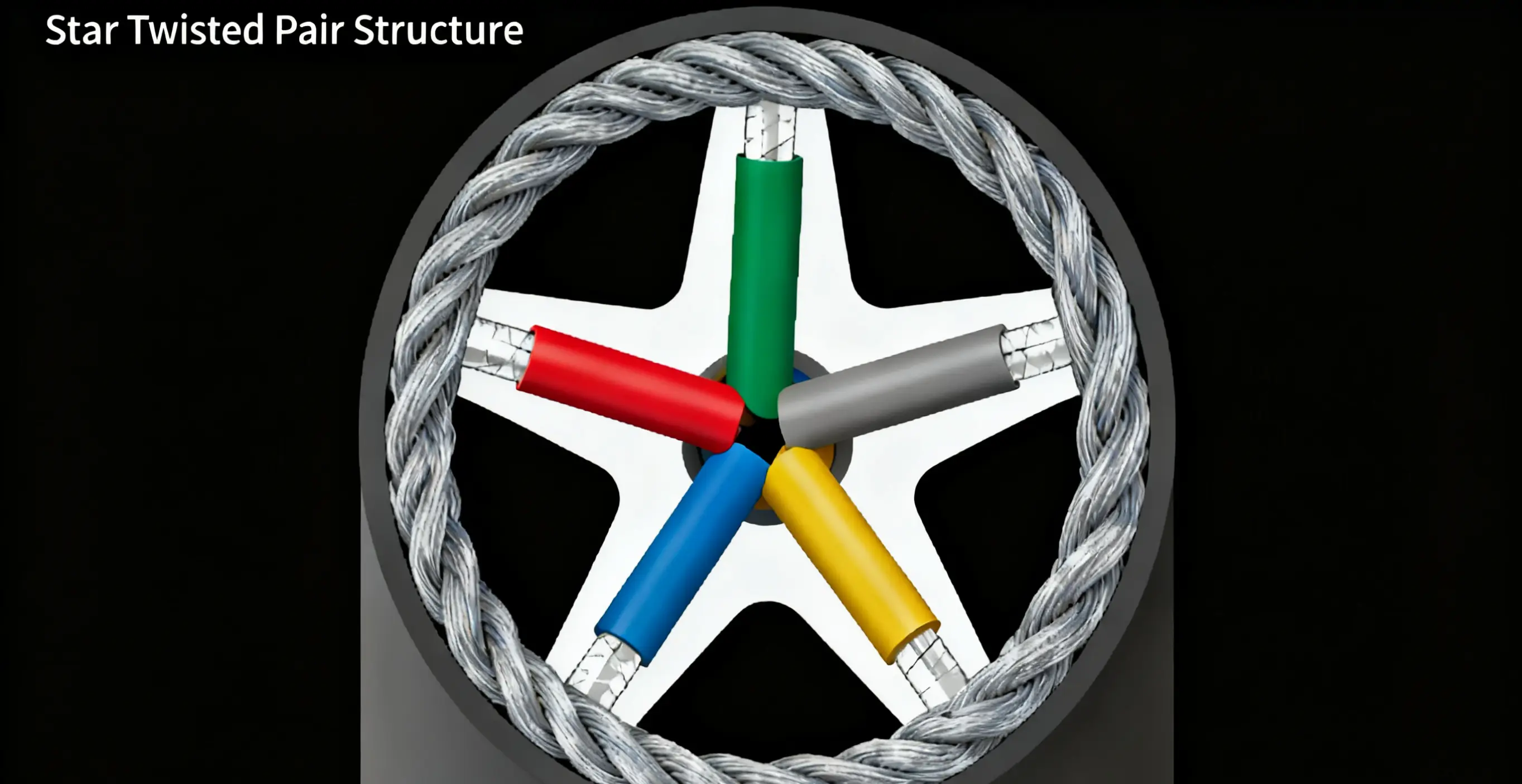

-
Stranding Parameter Optimization:
-
A "Star Quad Machine + Eccentricity Compensator" combination is used to control the stranding pitch (range 80-120mm, adjusted according to cable type), with pitch deviation ≤±2mm. An excessive pitch can lead to loose units, while too small a pitch increases signal attenuation.
-
The innovation of the Chinese solution: Real-time monitoring of the payoff tension of the 4 single wires (maintained consistently at 0.8-1.2 N) via tension sensors (accuracy ±0.1 N) prevents uneven core lengths due to tension imbalance, which can cause earth capacitance unbalance (Chinese processes can control capacitance unbalance to ≤30 pF/km, far lower than the common 50 pF/km in the Indian market).
-
-
Binder Yarn Reinforcement Control:
-
High-strength polyester binder yarn (breaking strength ≥5N) is selected. The binder yarn pitch is set to 1/3 of the stranding pitch (e.g., if the stranding pitch is 100 mm, the binder pitch is 33 mm), with tension controlled at 0.5-0.8 N—preventing the star quad from loosening during subsequent shielding processes.
-
Chinese equipment is equipped with a "Binder Yarn Tension Auto-compensation Device" that adjusts binder tension in real time based on unit diameter changes, achieving 100% binder coverage without missed or overlapping binds.
-
(B) Copper Shielding Unit Manufacturing Process and Equipment
Copper shielding is key to blocking external electromagnetic interference. Chinese technology, through "Corrugation Optimization + Shielding Integrity Control," achieves shielding effectiveness ≥85dB (at 1 1MHz), meeting the anti-interference requirements of Indian railway electrified sections.
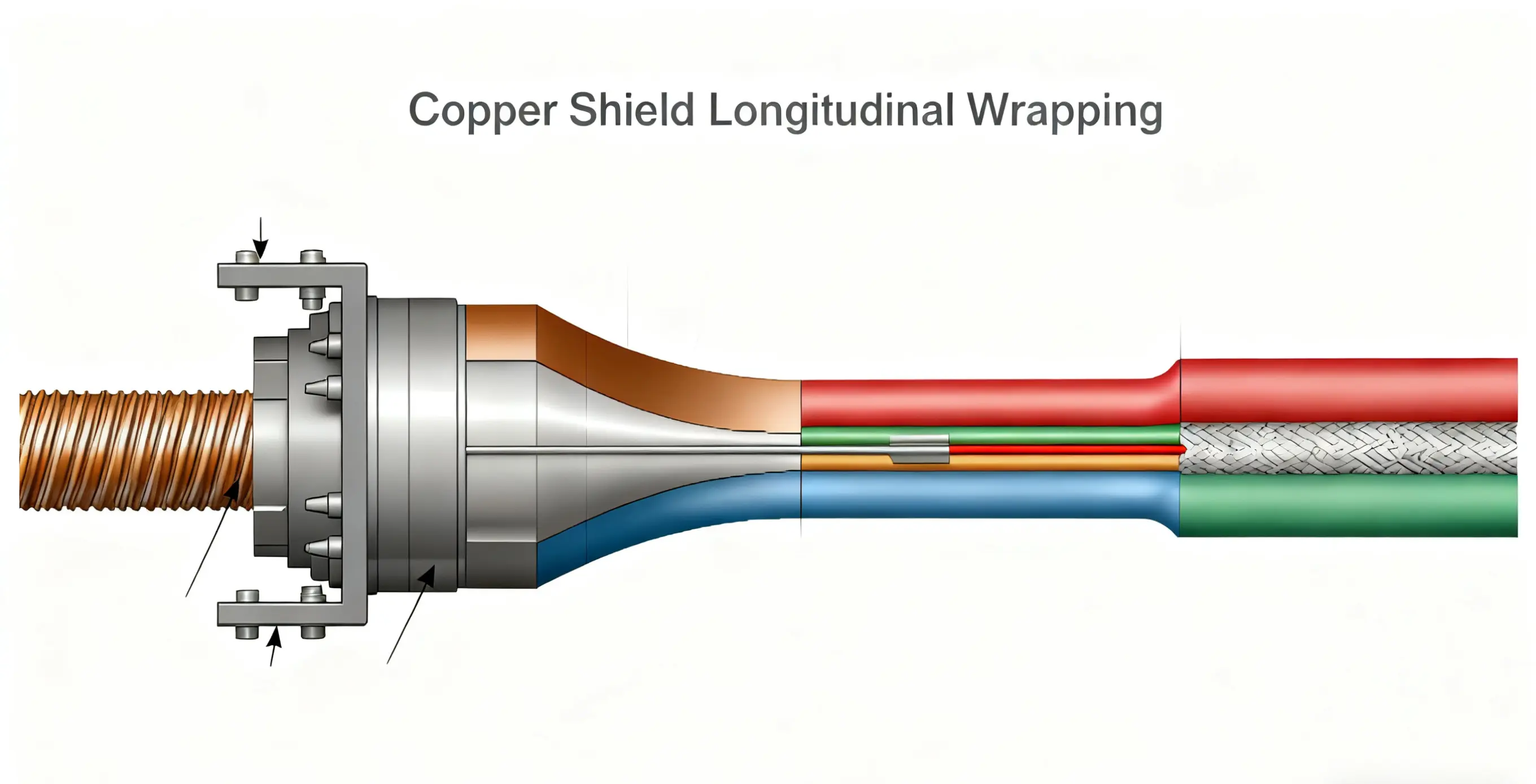
-
Copper Tape Corrugation Process:
-
Soft annealed copper tape with a thickness of 0.15-0.2mm (elongation ≥30%) is selected. Transverse corrugation is performed using a "Dual-Roll Corrugator" (corrugation depth 0.3-0.5mm, tooth pitch 1.5-2mm). Corrugation uniformity directly affects seam closure quality.
-
The corrugator in the Chinese solution is equipped with a "Copper Tape Guidance Correction Device" (deviation ≤±0.5mm), preventing the tape from deviating from the optimal engagement point when entering the longitudinal forming tool, which causes edge lift or folding. Simultaneously, the corrugator speed is synchronized with the main line speed (synchronization error ≤±1 m/min), preventing stretching or wrinkling of the copper tape due to speed mismatch.
-
-
Shielding Integrity Assurance:
-
Drain Wire Breakage Warning: Chinese manufacturers innovatively designed a "24V DC Alarm Device." A free-swinging lever rests on the drain wire; upon breakage, the lever falls, triggering contact closure, illuminating a warning light, and interlocking to stop the production line (response time ≤0.5s). This avoids sections without a drain wire, increasing process yield from 85% to over 99%.
-
Mesh Tape / PP Tape Sheathing: The longitudinal forming tool uses a "Bell-mouth Gradual Design" to guide the mesh tape (or PP tape) for uniform sheathing over the star quad, with an overlap ratio ≥15%. During tape change, the line speed is reduced to 60% of normal speed, employing "Hot Melt Bonding + Tape Reinforcement" (bonding length ≥50 mm) to prevent insulation layer puncture caused by mesh tape breakage.
-
-
Key Equipment Recommendation
The Chinese independently developed "PSB-1600 Copper Shielding Longitudinal Forming Production Line," which integrates the following core functions:-
Dual Reel Pay-off Device: Simultaneously pays off star quad (tension 0.6-1.0 N) and drain wire (tension 0.3-0.5 N), with tension fluctuation ≤ ±0.05 N.
-
Longitudinal Forming Temperature Control System: Controls PP tape forming temperature (180-200°C), ensuring firm bonding without bubbles.
-
Online Shielding Detection Device: Detects copper tape seam gap (≤0.1 mm) via eddy current sensor, triggering immediate alarm if out of tolerance.
-
III. Key Process: Cabling and Earth Capacitance Balance Control—The "Final Calibration" of Finished Product Performance
The cabling process involves stranding multiple shielded units into a cable core. Earth capacitance unbalance is a core indicator for evaluating cable anti-interference capability (the Chinese standard requires ≤40 pF/km; Indian high-speed rail projects typically require ≤50 pF/km). The Chinese solution achieves stable compliance with this indicator through "Reel Set Optimization + Structure Control."
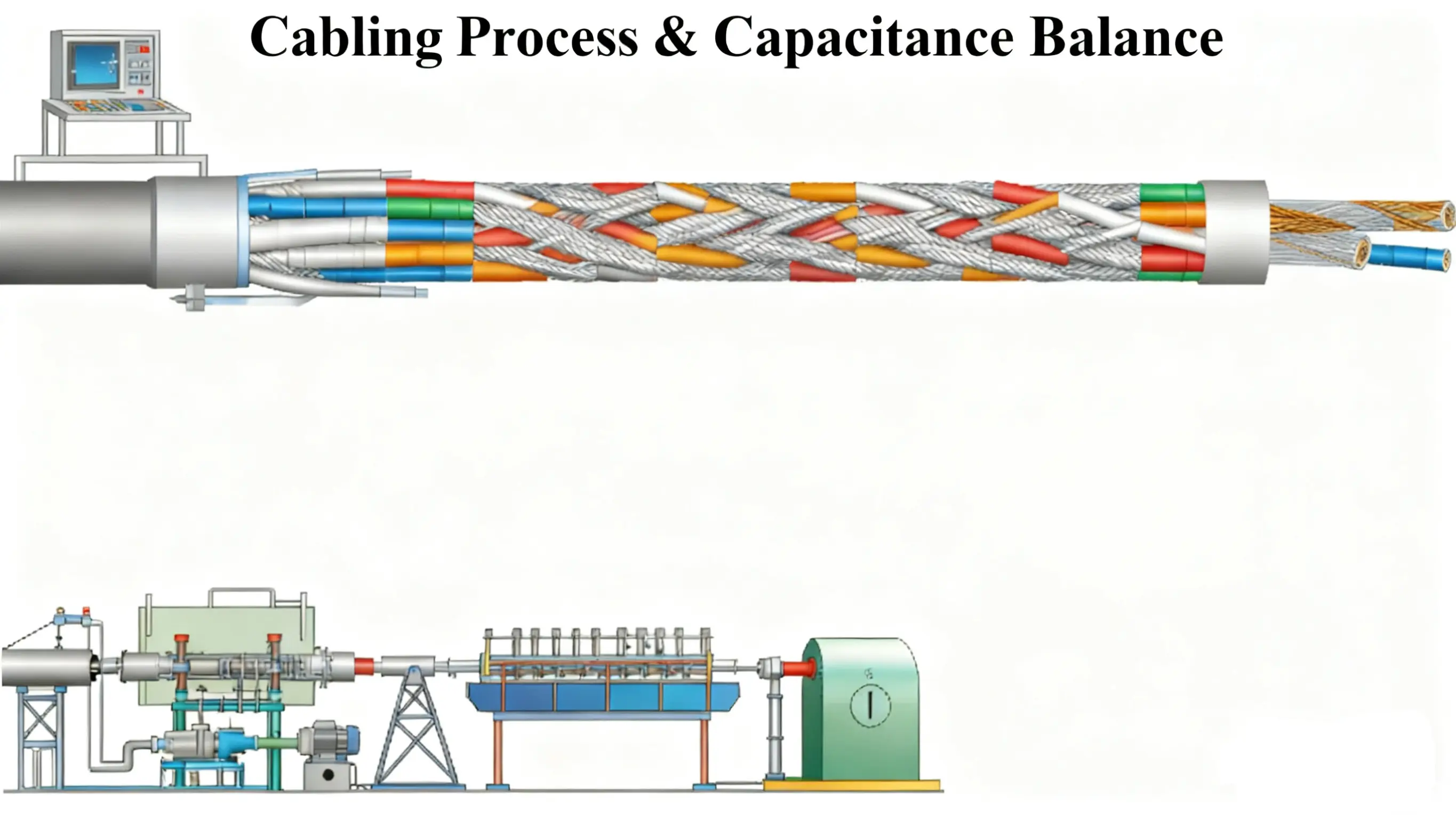
(A) Cabling Process Control Points
-
Shielded Unit Group Optimization (Reel Set Setup):
-
Each shielded unit group is first tested for earth capacitance (using Chinese-made "KZC-III Capacitance Coupling Tester," frequency 0.8-1.0 kHz, accuracy ±1 pF). Units are grouped according to capacitance value (deviation within group ≤5 pF/km). During cabling, a "staggered arrangement of high and low capacitance values" is adopted – utilizing complementary cancellation to control the overall cable capacitance unbalance to ≤35 pF/km, preventing finished product failure due to a single unit's capacitance exceeding the standard.
-
-
Aluminum Sheath and Cable Core Gap Control:
-
During aluminum sheath extrusion (aluminum tape thickness 0.25-0.3mm), the gap between the aluminum sheath and the cable core (≤1mm) is controlled through "Extruder - Caterpillar Haul-off Speed Synchronization" (synchronization error ≤±0.5 m/min). A gap that is too small can easily cause core deformation, while too large a gap increases signal attenuation.
-
The "Sheath Thickness Online Monitor" (accuracy ±0.02mm) equipped on Chinese devices allows for real-time adjustment of extruder die head pressure, ensuring uniform aluminum sheath thickness and further enhancing anti-interference performance.
-
(B) Finished Product Testing Technology
The Chinese solution emphasizes "Full-Process Testing." In addition to routine appearance and dimensional checks, the following electrical performance tests are crucial:
-
Earth Capacitance Unbalance Test: Convert to per km value using the formula (, is measured length) to ensure compliance.
-
Capacitance Coupling Coefficient (K₁) Test: Control K₁ value ≤80 pF/km (Chinese process can stabilize at ≤60 pF/km) to prevent signal crosstalk.
-
High Voltage Test: Apply 2.5 kV power frequency voltage for 1 minute, with no breakdown or flashover, ensuring reliable insulation performance.
IV. Core Advantages of the Chinese Technical Solution – Creating Practical Value for Indian Manufacturers
Compared to traditional Indian production processes, the Chinese solution offers significant advantages in the three key dimensions of "Efficiency, Quality, Cost," directly addressing pain points for Indian manufacturers:
|
Dimension |
Chinese Technical Solution |
Traditional Indian Process |
Value Enhancement Point |
|
Production Efficiency |
Fully automated production line, daily capacity ≥5 km |
Semi-automated production, daily capacity ≤2 km |
Capacity increased by 150%, labor cost reduced by 40% |
|
Product Quality |
Earth capacitance unbalance ≤35 pF/km, yield rate ≥99% |
Earth capacitance unbalance ≥50 pF/km, yield rate ≤85% |
Reduces losses from non-conforming products, meets HSR project requirements |
|
Cost Control |
Die life increased 5x, consumable waste reduced by 30% |
Frequent die replacement, consumable waste ≥50% |
Comprehensive production cost reduced by 25%-30% |
|
Environmental Compliance |
Wastewater pretreatment system (heavy metal removal rate ≥99%) |
Mostly direct discharge, high environmental risk |
Complies with Indian Environmental Protection Act emission standards |
V. Conclusion: Partnering with Chinese Technology to Accelerate Indian Railway Signal Upgrades
Chinese railway signal cable technology has achieved the leap "from following to leading." Its process maturity, equipment reliability, and cost advantages can help Indian manufacturers quickly overcome production bottlenecks – whether in the precision manufacturing of insulated single wires, the anti-interference optimization of copper shielding, or the balance control of earth capacitance, the Chinese solution provides a one-stop service of "Process + Equipment + Materials + After-sales". Currently, China has exported over 50 railway signal cable production lines to regions including Southeast Asia and Africa, assisting in local railway digital transformation.
For Indian manufacturers, adopting Chinese technology can not only enhance product quality and reduce production costs but also leverage the global experience of Chinese high-speed rail to meet the future development needs of high-speed and intelligent railways in India. We look forward to partnering with Indian counterparts, using advanced technology to jointly build a reliable and efficient railway signal transmission network, injecting strong momentum into the development of Indian railways.











